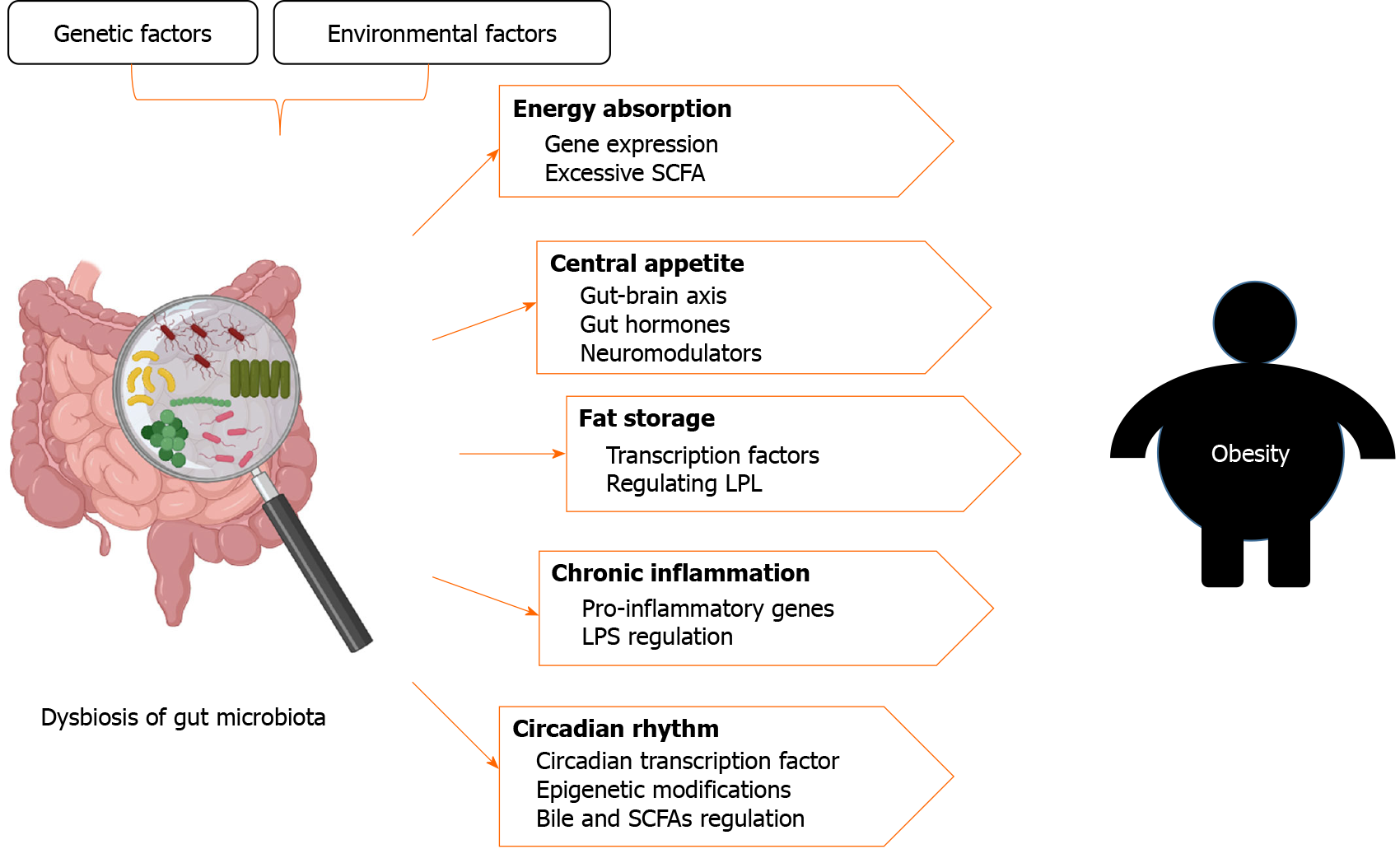
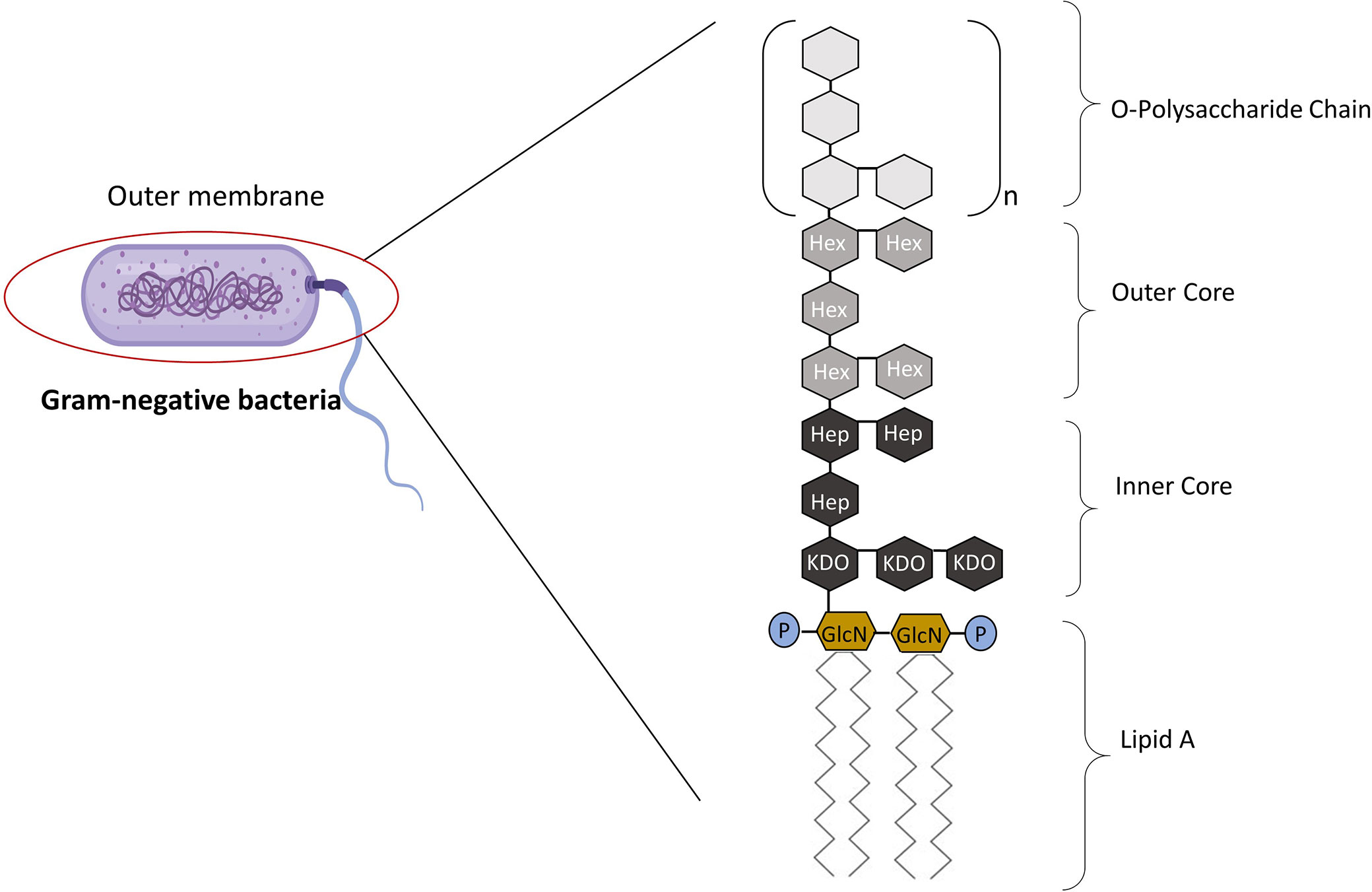
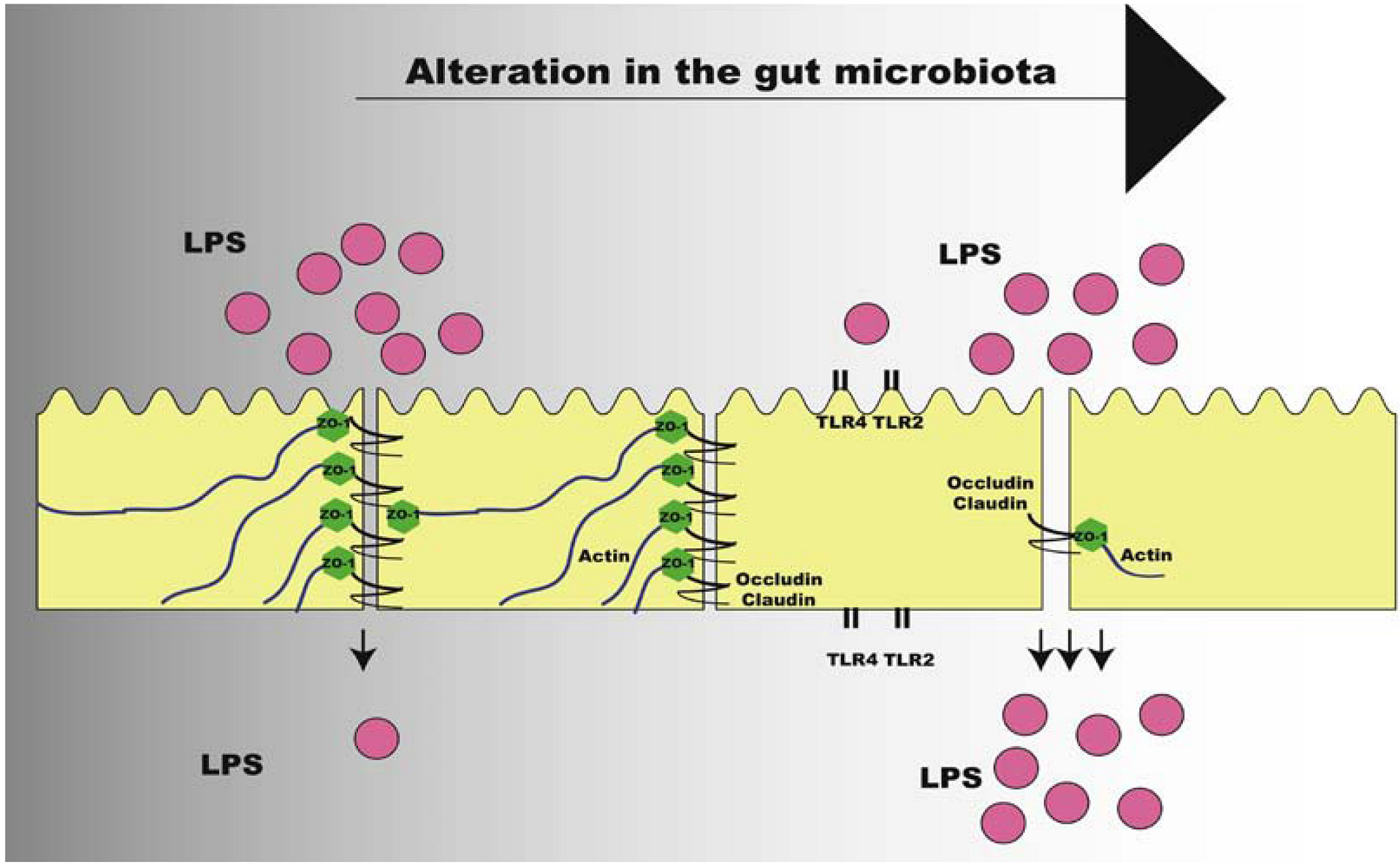
Obesity, high-fat diet, and diabetes are associated with higher gut... | Download Scientific Diagram

Asperuloside Improves Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes through Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Signaling - ScienceDirect

Engineering the Gut Microbiome for Treatment of Obesity: A Review of Current Understanding and Progress - Lim - 2020 - Biotechnology Journal - Wiley Online Library

Engineering the Gut Microbiome for Treatment of Obesity: A Review of Current Understanding and Progress - Lim - 2020 - Biotechnology Journal - Wiley Online Library
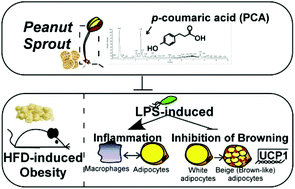
Peanut sprout rich in p-coumaric acid ameliorates obesity and lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and the inhibition of browning in adipocytes via mitochondrial activation - Food & Function (RSC Publishing)
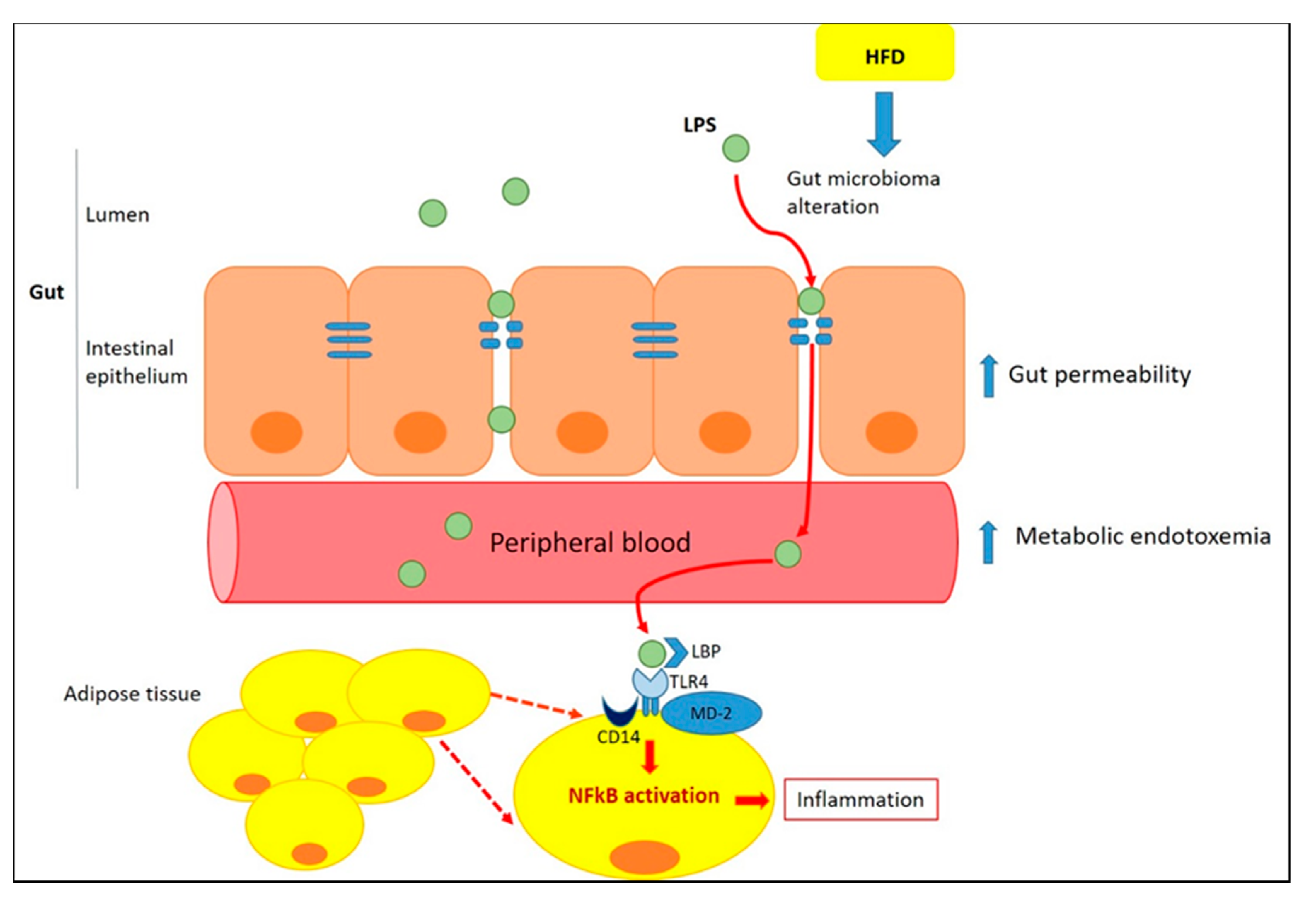
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Potential of Nutraceutical Supplementation in the Modulation of White and Brown Fat Tissues in Obesity-Associated Disorders: Role of Inflammatory Signalling
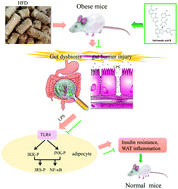
Salvianolic acid B prevents body weight gain and regulates gut microbiota and LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway in high-fat diet-induced obese mice - Food & Function (RSC Publishing)
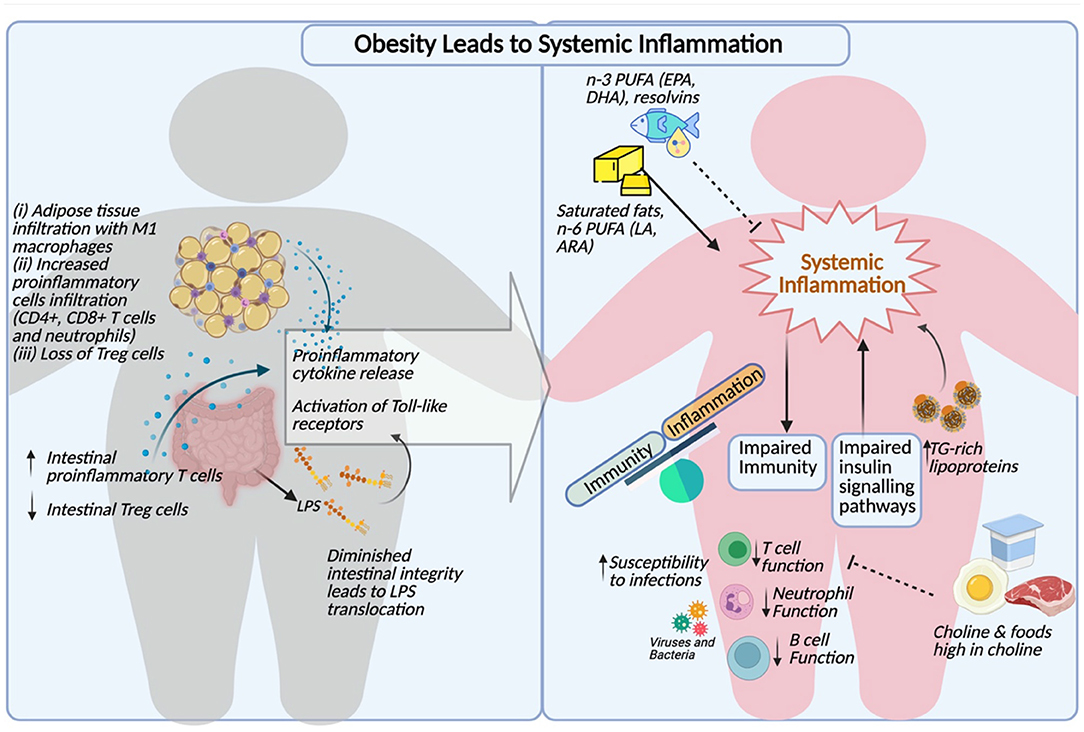
Frontiers | The Interplay of Obesity, Dyslipidemia and Immune Dysfunction: A Brief Overview on Pathophysiology, Animal Models, and Nutritional Modulation

Metabolic endotoxemia promotes adipose dysfunction and inflammation in human obesity | American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism

SciELO - Brasil - Translational research into gut microbiota: new horizons on obesity treatment: updated 2014 Translational research into gut microbiota: new horizons on obesity treatment: updated 2014

Understanding the Role of the Gut Microbiome and Microbial Metabolites in Obesity and Obesity-Associated Metabolic Disorders: Current Evidence and Perspectives | SpringerLink
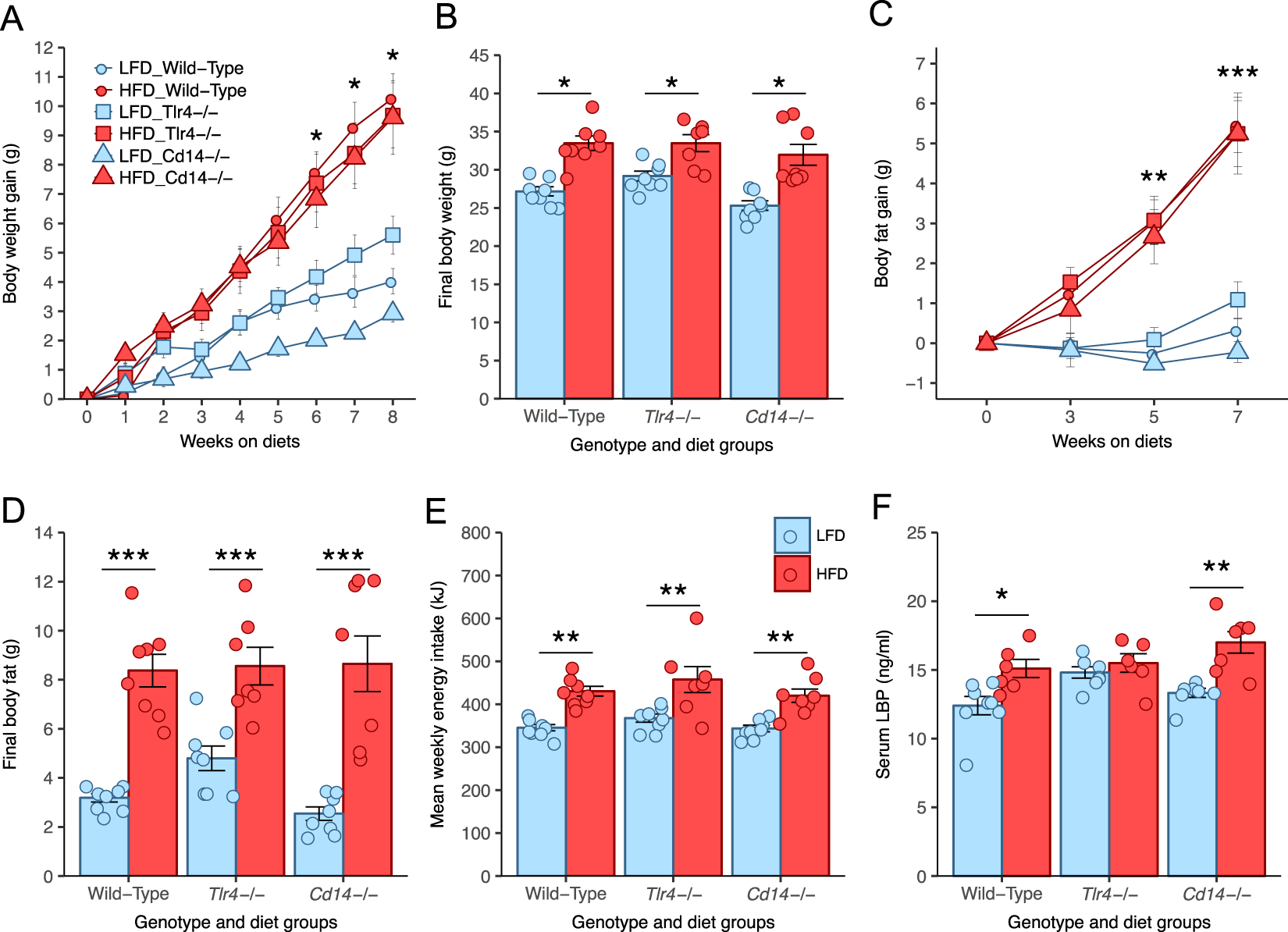
Diet induced obesity is independent of metabolic endotoxemia and TLR4 signalling, but markedly increases hypothalamic expression of the acute phase protein, SerpinA3N | Scientific Reports

Beneficial Effects of Dietary Polyphenols on High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Linking with Modulation of Gut Microbiota | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry


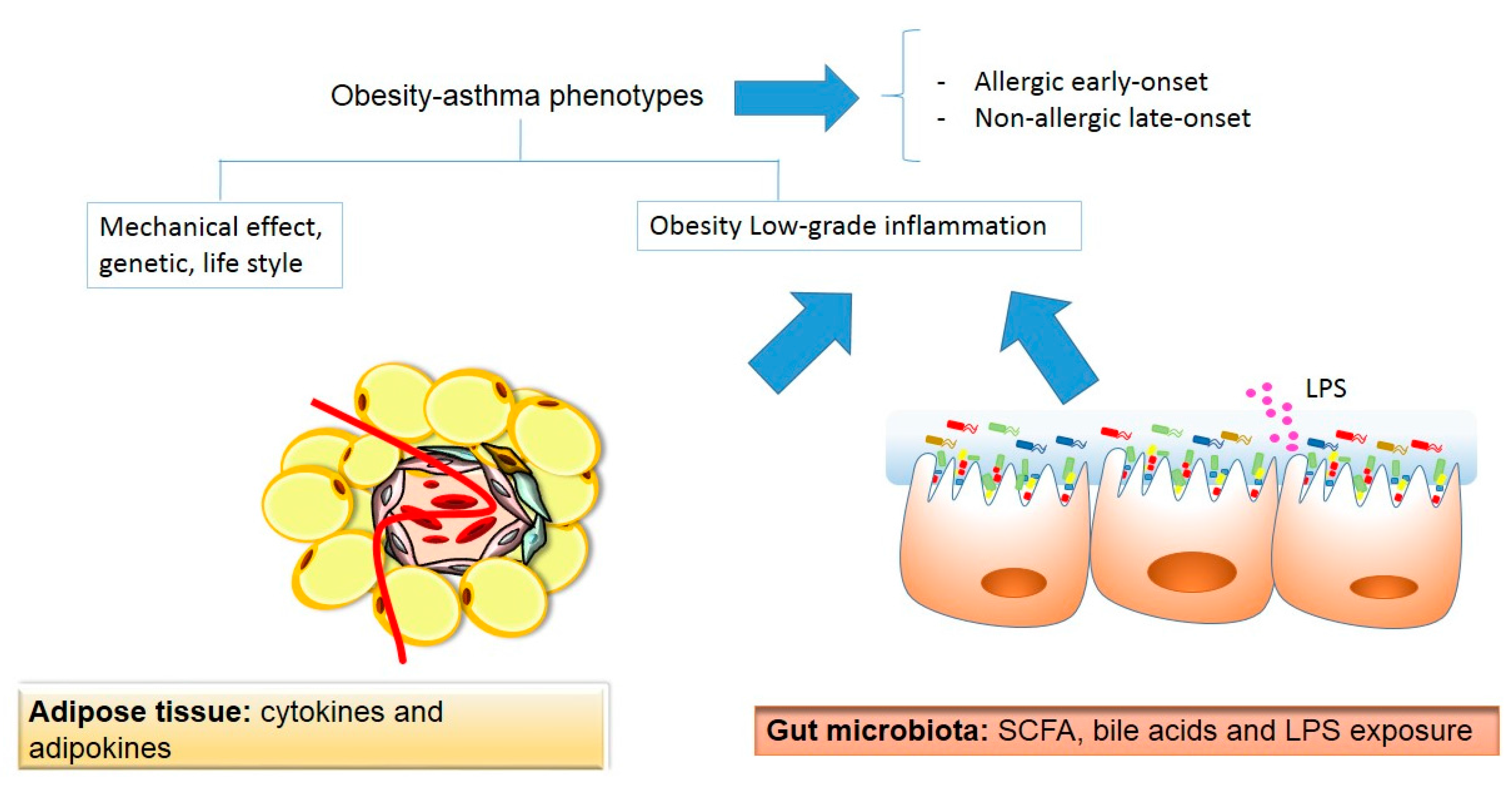
![Figure 7: [Schematic diagram illustrating the possible...]. - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf Figure 7: [Schematic diagram illustrating the possible...]. - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556470/bin/obesity_endocr_gut-Image007.jpg)